
Single entry accounting records only one side of a transaction, usually focusing on cash inflows and outflows, which gives a limited view of financial position. Double entry accounting, in contrast, records both aspects of a transaction – debits and credits – ensuring that the accounting equation remains double entry accounting balanced. As a result, double entry provides a more complete, accurate, and reliable financial record than single entry. The double-entry accounting system records each financial transaction in at least two accounts, ensuring that total debits always equal total credits.

In other words, why is this bookkeeping method so important?
A transaction could be anything from a client receiving payment to purchasing supplies to accruing interest on a loan. Real accounts mean assets owned by a business such as a machinery, equipment, land, property, and so on. When a company’s software prepares a check, the software will automatically reduce the Cash account.
- Double-entry bookkeeping requires that every transaction be recorded in at least two accounts, ensuring that the accounting equation remains balanced.
- This principle states that every transaction affects at least two accounts, with one account being debited and another account being credited.
- However, it requires accounting knowledge and skills to pursue that some individuals and small businesses may not be available.
- At the heart of double entry accounting lies the pivotal concept that every financial transaction has two distinct and inseparable effects.
- Journalizing is the initial process of recording a business transaction in the general journal, using the rules of debits and credits.
Single vs. double-entry bookkeeping

Your general ledger is a record that sorts and summarizes your business transactions. You can use your general ledger to see where money is coming from and where it is Grocery Store Accounting going. With a general ledger, you can also see the amount of cash you have on hand and how much debt your business has. The double-entry bookkeeping method is based on the idea that every business transaction has equal and opposite effects on at least two accounts.
- Liabilities include bank loans, accounts payable, and any other forms of debt.
- Non-profit organizations find double-entry accounting invaluable for maintaining transparency and accountability.
- The process begins with identifying the transaction, which involves recognizing the nature of the activity and the accounts that will be affected.
- It was first documented by Luca Pacioli, an Italian mathematician and Franciscan friar, in his book “Summa de Arithmetica, Geometria, Proportioni et Proportionalita” in 1494.
- Here, we’ll explore the basics of double-entry accounting, provide examples and solutions, and explain why this method is essential for effective bookkeeping.
- The double-entry system ensures every financial transaction affects at least two accounts, with one account debited and another credited.
What is Double-Entry Bookkeeping?
As time passes and you make loan repayments, you would record additional debits and credits to accurately track the loan balance and interest expenses. Implementing double-entry accounting practices is a strategic decision that can significantly enhance the financial management of any business. By adopting this method, organizations can ledger account ensure that their financial records are accurate, reliable, and provide a comprehensive view of their financial health. This foundational practice not only supports effective decision-making but also fosters a culture of accountability and transparency. The use of accounting software can alleviate some of the complexity, but it still requires users to be familiar with the underlying principles of double-entry accounting. Learning to navigate these systems effectively can take time, as users must understand how the software translates transactions into the appropriate journal entries and financial statements.
Financial statement preparation 🔗
This dual recording helps to prevent errors and omissions, as discrepancies can be easily identified through the balancing of accounts. The accounting records through journal entries form the basis of financial statements. Double-entry bookkeeping is more than just a method for recording transactions; it is a structured system that provides clarity and accuracy in financial reporting. Understanding how this system works is essential for managing business finances effectively.
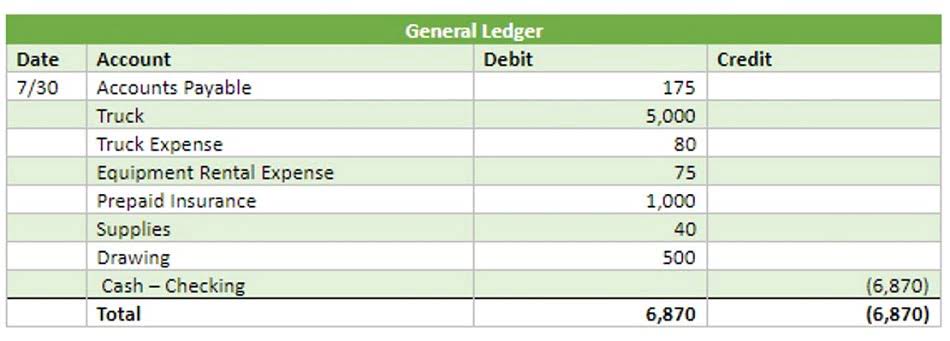
Lastly, organizations that prioritize financial analysis and strategic planning should adopt the double-entry system. The detailed records maintained through this method allow for in-depth analysis of financial performance, enabling businesses to identify trends and make data-driven decisions. Moreover, the systematic nature of double-entry bookkeeping enhances the ability to track financial trends and patterns. By maintaining consistent records, businesses can analyze historical data to identify areas of growth or concern. This analysis supports strategic planning and resource allocation, ultimately driving better financial outcomes. Additionally, the systematic nature of double-entry accounting promotes meticulous record-keeping.
A unique account number and name represent each account in a company’s chart of accounts. The double-entry system ensures every financial transaction affects at least two accounts, with one account debited and another credited. This system helps ensure accuracy and prevent fraud by providing checks and balances for every transaction. Double-entry accounting records every transaction with two parts—debit and credit—to keep financial statements accurate and balanced. This equation, also known as the balance sheet equation, is used to calculate the balance of each account in a company’s financial records.
